SpringBoot之自定義啟動(dòng)異常堆棧信息打印方式
在SpringBoot項(xiàng)目啟動(dòng)過(guò)程中,當(dāng)一些配置或者其他錯(cuò)誤信息會(huì)有一些的規(guī)范的提示信息
***************************APPLICATION FAILED TO START***************************
Description:
Web server failed to start. Port 8080 was already in use.
Action:
Identify and stop the process that’s listening on port 8080 or configure this application to listen on another port.
在SpringBoot 中其實(shí)現(xiàn)原理是什么,我們?cè)撊绾巫远x異常信息呢
1、SpringBoot異常處理的源碼分析在springboot啟動(dòng)的核心方法run中會(huì)加載所有的SpringBootExceptionReporter
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
調(diào)用了getSpringFactoriesInstances方法
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) { ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader(); // Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); return instances; }
其主要通過(guò)Spring的Factories機(jī)制來(lái)加載
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); configureHeadlessProperty(); SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); context = createApplicationContext(); exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); refreshContext(context); afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } listeners.started(context); callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable ex) { //異常捕獲中,向用戶打印異常信息 handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { listeners.running(context); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return context; }
在try catch中,catch會(huì)打印異常信息
private void handleRunFailure(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception, Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners) { try { try { handleExitCode(context, exception); if (listeners != null) { listeners.failed(context, exception); } } finally { reportFailure(exceptionReporters, exception); if (context != null) { context.close(); } } } catch (Exception ex) { logger.warn('Unable to close ApplicationContext', ex); } ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(exception); }
private void reportFailure(Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters, Throwable failure) { try { for (SpringBootExceptionReporter reporter : exceptionReporters) { if (reporter.reportException(failure)) { registerLoggedException(failure); return; } } } catch (Throwable ex) { // Continue with normal handling of the original failure } if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) { logger.error('Application run failed', failure); registerLoggedException(failure); } }
遍歷exceptionReporters,打印日常信息
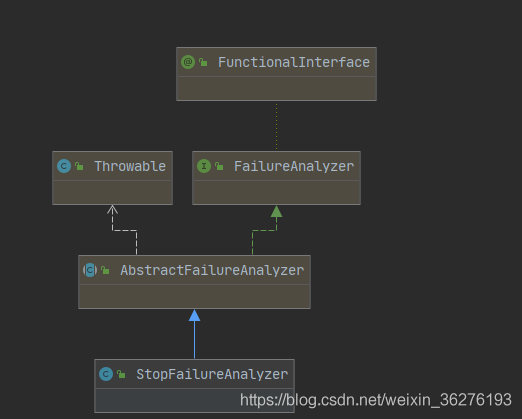
SpringBootExceptionReporter是一個(gè)回調(diào)接口,用于支持對(duì)SpringApplication啟動(dòng)錯(cuò)誤的自定義報(bào)告。里面就一個(gè)報(bào)告啟動(dòng)失敗的方法。
其實(shí)現(xiàn)類:org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers
用于觸發(fā)從spring.factories加載的FailureAnalyzer和FailureAnalysisReporter實(shí)例。
2、如何自定義異常信息/** * <p> * * <p> * * @author: xuwd * @time: 2020/11/16 10:52 */public class WannaStopException extends RuntimeException {}
自定義異常信息打印
public class StopFailureAnalyzerextends AbstractFailureAnalyzer<WannaStopException> { @Override protected FailureAnalysis analyze(Throwable rootFailure, WannaStopException cause) {for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : cause.getStackTrace()) { if (stackTraceElement.getClassName().equals('com.pigx.demo.Config21')) {return new FailureAnalysis('A想停止', '別要A了', cause); }}return null; }}
接下來(lái)令他生效,通過(guò)上面分析可以可看出需要通過(guò)AutoConfigurationImportSelector,類似于自定義SpringBoot Starter AutoConfiguration的形式,我們需要在META-INF/spring.factories文件內(nèi)進(jìn)行定義,如下所示:

接著在合適的地方拋出WannaStopException 異常
總結(jié)在springboot 啟動(dòng)過(guò)程中會(huì)先對(duì)異常信息進(jìn)行補(bǔ)捕獲,對(duì)進(jìn)行日志格式處理的日志進(jìn)行處理;其核心是通過(guò)SpringBootExceptionReporter回調(diào)及sping-spi bean的管理。
以上為個(gè)人經(jīng)驗(yàn),希望能給大家一個(gè)參考,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)。
相關(guān)文章:
1. IntelliJ IDEA導(dǎo)入jar包的方法2. SSM框架JSP使用Layui實(shí)現(xiàn)layer彈出層效果3. 刪除docker里建立容器的操作方法4. IntelliJ IDEA導(dǎo)出項(xiàng)目的方法5. java使用xfire搭建webservice服務(wù)的過(guò)程詳解6. .Net中的Http請(qǐng)求調(diào)用詳解(Post與Get)7. JS如何在數(shù)組指定位置插入元素8. PHP下對(duì)緩沖區(qū)的控制9. Vue 實(shí)現(xiàn)對(duì)quill-editor組件中的工具欄添加title10. Java源碼解析之ClassLoader

 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備