SpringBoot結(jié)合JSR303對(duì)前端數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行校驗(yàn)的示例代碼
一、校驗(yàn)分類
數(shù)據(jù)的校驗(yàn)一般分為**前端校驗(yàn)、后端校驗(yàn)**
二、前端校驗(yàn)
前端校驗(yàn)是最為明顯的,先說一下:
① HTML
非空校驗(yàn) 如 HTML5 新增的屬性required='true',一旦沒有填寫就輸入框就顯示紅色,具體使用如:
<input type='text' name='name' required='true'/>
② JS
同時(shí)在提交表單發(fā)送 Ajax請(qǐng)求 的時(shí)候,來個(gè) onSubmit 函數(shù),具體例如(使用點(diǎn) EasyUI ):
function submitData(){$('#fm').form('submit',{url:'/admin/film/save',onSubmit:function(){var content=CKEDITOR.instances.content.getData();if(content==''){$.messager.alert('系統(tǒng)提示','內(nèi)容不能為空!');return false;}return $(this).form('validate');},success:function(result){var result=eval(’(’+result+’)’);if(result.success){$.messager.alert('系統(tǒng)提示','保存成功!');resetValue();}else{$.messager.alert('系統(tǒng)提示','保存失敗!');}}});}
但我們都知道,這是防君子不防小人的做法,用戶可以使用 F12,查看源碼,修改關(guān)鍵部位的代碼,如把 required='true' 刪除掉,就可以提交表單了。所以前端作用雖然明顯,但是數(shù)據(jù)處理方面,真正用處并不大。
三、后端校驗(yàn)
前面說了那么多,就是為了引出 后端校驗(yàn) 這一話題。數(shù)據(jù)是否提交到數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)中去,就看后端的代碼了。后端校驗(yàn),主要實(shí)施在 JavaBean、Controller 中。下面列舉一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的例子,從代碼中說明一切。
① 代碼結(jié)構(gòu)圖
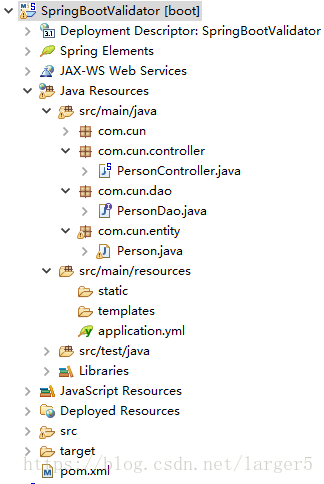
② entity
實(shí)體屬性部位空,一般使用如 @NotEmpty(message='請(qǐng)輸入用戶名!') ,這樣既不能為 空 ,也不能為null
package com.cun.entity;import javax.persistence.Column;import javax.persistence.Entity;import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;import javax.persistence.Id;import javax.persistence.Table;import javax.validation.constraints.Max;import javax.validation.constraints.Min;import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;import javax.validation.constraints.Null;import javax.validation.constraints.Size;import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotBlank;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;@Entity@Table(name = 't_person')public class Person {@Id@GeneratedValue@ApiModelProperty(value = '用戶id')private Integer id;@NotBlank(message = '用戶名不能為空') // 為''/’’都不行@Size(min = 2, max = 30, message = '2<長(zhǎng)度<30')@Column(length = 50)@ApiModelProperty(value = '用戶名')private String userName;@NotNull(message = '用戶密碼不能為空')@Column(length = 50)@ApiModelProperty(value = '用戶密碼')private String password;@Max(value = 150, message = 'age應(yīng)<150') // 數(shù)字@Min(value = 1, message = 'age應(yīng)>1') // 數(shù)字@NotNull(message = '年齡不能為空')@ApiModelProperty(value = '用戶年齡')private Integer age;@NotNull(message = '郵箱不為空')@Email(message = '郵件格式不對(duì)')@Column(length = 100)@ApiModelProperty(value = '用戶郵箱')private String email;// 使用 JPA 必備public Person() {super();}public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getUserName() {return userName;}public void setUserName(String userName) {this.userName = userName;}public String getPassword() {return password;}public void setPassword(String password) {this.password = password;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public String getEmail() {return email;}public void setEmail(String email) {this.email = email;}}
③ dao
其實(shí)也沒什么代碼,這就是 JPA 的強(qiáng)大之處
package com.cun.dao;import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;import com.cun.entity.Person;public interface PersonDao extends JpaRepository<Person, Integer>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Person> {}
④ Service、ServiceImpl (省略)
⑤ Controller
package com.cun.controller;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;import javax.validation.Valid;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import com.cun.dao.PersonDao;import com.cun.entity.Person;import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;@RestController@RequestMapping('/person')@EnableSwagger2public class PersonController {@Autowiredprivate PersonDao personDao;@PostMapping('/insert')public Map<String, Object> insertPerson(@Valid Person person, BindingResult bindingResult) {Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {List<ObjectError> errorList = bindingResult.getAllErrors();List<String> mesList=new ArrayList<String>();for (int i = 0; i < errorList.size(); i++) {mesList.add(errorList.get(i).getDefaultMessage());}map.put('status', false);map.put('error', mesList);} else {map.put('status', true);map.put('msg', '添加成功');personDao.save(person);}return map;}}
⑥ yml
server: port: 80 #為了以后訪問項(xiàng)目不用寫端口號(hào) context-path: / #為了以后訪問項(xiàng)目不用寫項(xiàng)目名spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot username: root password: 123 jpa: hibernate: ddl-auto: update #數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)同步代碼 show-sql: true #dao操作時(shí),顯示sql語(yǔ)句
⑦ POM
使用 SpringBoot Starter 導(dǎo)入 JPA、MySQL
使用 Swagger 演示
<!-- swagger生成接口API --><dependency><groupId>io.springfox</groupId><artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId><version>2.7.0</version></dependency><!-- 接口API生成html文檔 --><dependency><groupId>io.springfox</groupId><artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId><version>2.6.1</version></dependency>
四、演示
輸入 http://localhost/swagger-ui.html 進(jìn)入接口測(cè)試站點(diǎn)
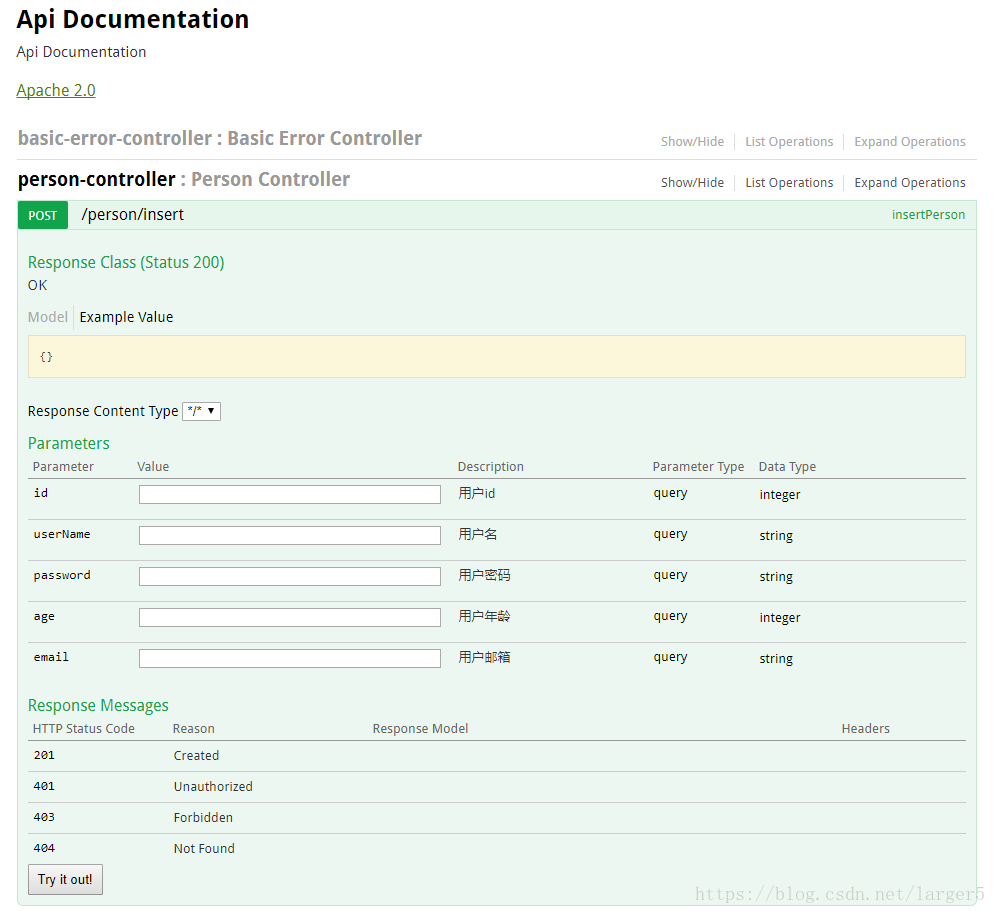
什么都沒有填寫,直接點(diǎn)擊Try it out!,可以看到返回給前端的 JSON 數(shù)據(jù),這時(shí)候數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)據(jù)是沒有改動(dòng)的,一條sql 語(yǔ)句都沒有執(zhí)行

當(dāng)然還可以進(jìn)行其他測(cè)試,這里就省略了
到此這篇關(guān)于SpringBoot結(jié)合JSR303對(duì)前端數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行校驗(yàn)的示例代碼的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)SpringBoot JSR303校驗(yàn)內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. 前端ajax請(qǐng)求+后端java實(shí)現(xiàn)的下載zip壓縮包功能示例2. ASP.NET MVC實(shí)現(xiàn)登錄后跳轉(zhuǎn)到原界面3. python解包概念及實(shí)例4. ASP基礎(chǔ)入門第四篇(腳本變量、函數(shù)、過程和條件語(yǔ)句)5. 快速一鍵生成Python爬蟲請(qǐng)求頭6. python中復(fù)數(shù)的共軛復(fù)數(shù)知識(shí)點(diǎn)總結(jié)7. React中的useEffect四種用法分享8. python析構(gòu)函數(shù)用法及注意事項(xiàng)9. python sys.stdin和sys.stdout的用法說明10. .NET使用StackTrace獲取方法調(diào)用信息的代碼演示

 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備