Spring源碼解析之Configuration
<!--logback-test.xml,配置不打印日志--><?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?><configuration> <include resource='org/springframework/boot/logging/logback/base.xml' /> <logger name='org.springframework' level='OFF'/></configuration>
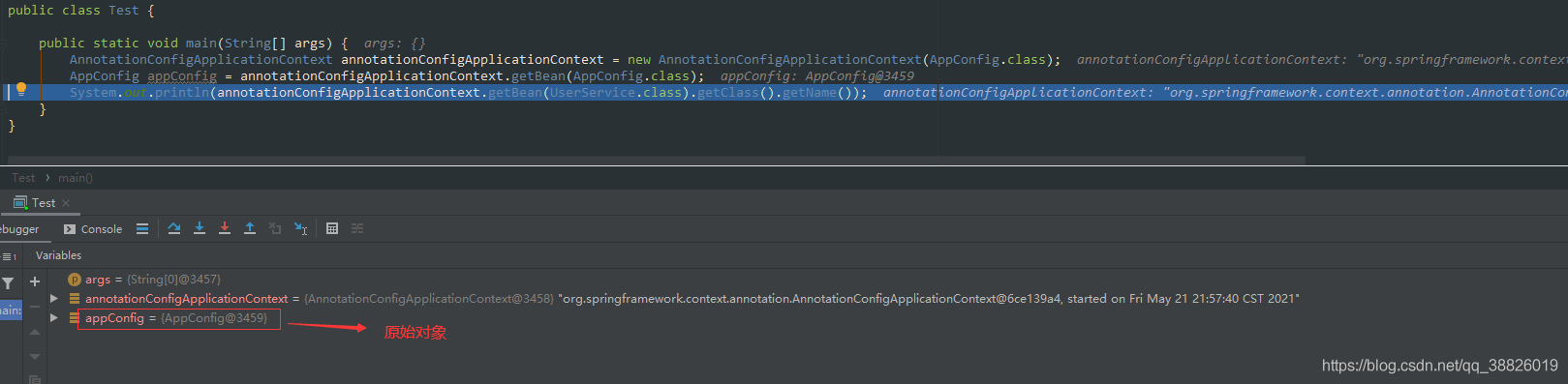
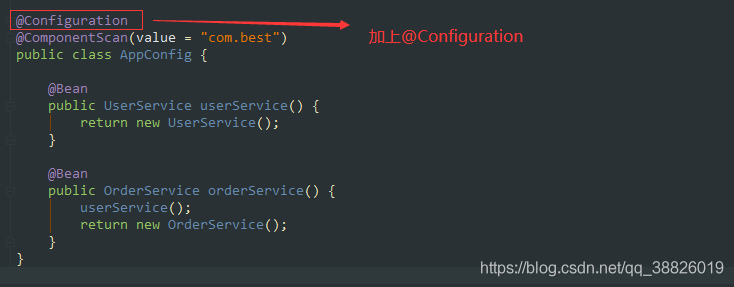
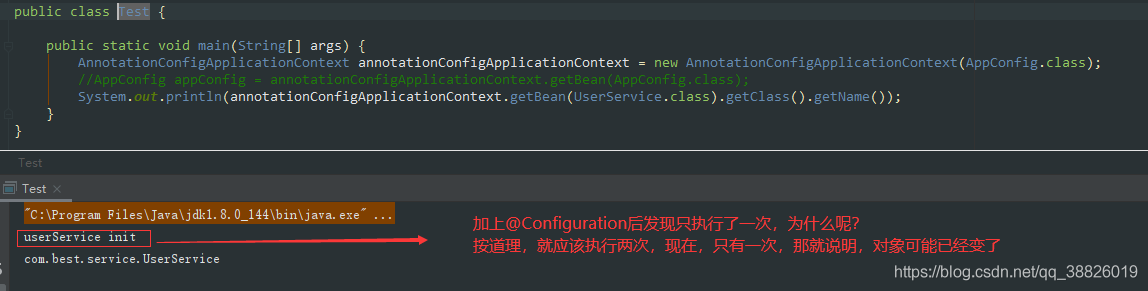
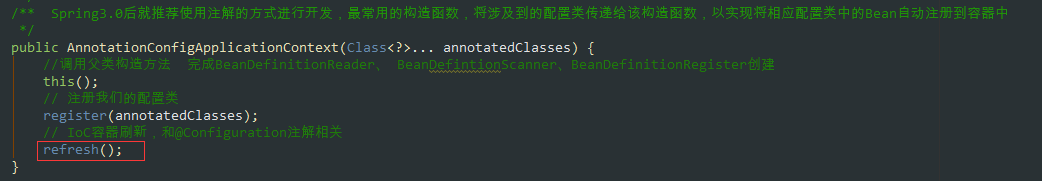
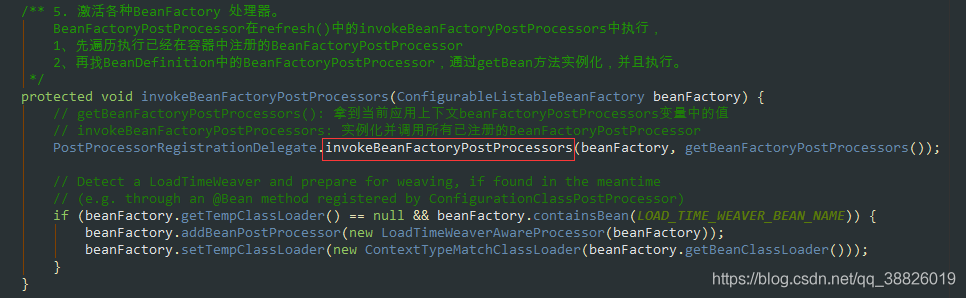
@Overridepublic void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {// 同步,線程安全; 防止 fresh還沒結(jié)束 就又進(jìn)入改方法 導(dǎo)致容器初始化錯(cuò)亂synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {// 準(zhǔn)備刷新 記錄開始時(shí)間 設(shè)置幾個(gè)標(biāo)志位 驗(yàn)證環(huán)境屬性prepareRefresh(); // 告訴子類刷新內(nèi)部bean工廠 創(chuàng)建BeanFactory 并且獲取BeanDefinition的定義信息/** *obtainFreshBeanFactory();方法 *解析為一個(gè)個(gè)beanDefinition 放在我們beanDefinitionMap中管理起來 * 1. refreshBeanFactory(); 核心方法 * AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory() * 創(chuàng)建DefaultListableBeanFactory 并設(shè)置屬性 * 加載BeanFactory; 根據(jù)不同的類型,調(diào)用不同的方法 * org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory) */ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // 準(zhǔn)備在這種情況下使用的bean工廠 向beanFactory中設(shè)置一些屬性 。對(duì)BeanFactory 進(jìn)行各種功能填充prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {// 允許在上下文 的子類中對(duì)bean工廠進(jìn)行后處理 由子類去實(shí)現(xiàn); 主要是自定義去使用postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // 第5步 【BeanFactoryPostProcessors ;bean工廠后置處理器】調(diào)用我們的bean工廠后置處理器 (所有實(shí)現(xiàn)接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的)//主要是// 會(huì)在此將class掃描成BeanDefinition 并注冊(cè)bean 到一個(gè)BeanDefinitionMap中 這個(gè)過程使用到代理//BeanFactoryPostProcessor 可以 用于容器完成初始化()// 此處可以 還沒有實(shí)例化Bean之前讀取Bean的信息,并作出一些修改。// 例如修改Bean的屬性,修改Bean的scope等invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); //https://blog.csdn.net/caihaijiang/article/details/35552859// 【BeanPostProcessors ;bean后置處理器】 注冊(cè)BeanPostProcessor// BeanPostProcessor是Bean的后置處理器,// 在Bean的初始化方法[InitializingBean 以及init-method]前,后執(zhí)行。registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // 為上下文初始化Message 源, 即不同語言的消息體, 國際化處理 i18ninitMessageSource(); // 初始化事件傳播器//初始化應(yīng)用消息廣播器, 并放入'applicationEventMulticaster' bean 中initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // 擴(kuò)展的一個(gè)實(shí)現(xiàn) ,留給子類來初始化其它的Bean。如springboot內(nèi)嵌的tomcat在這個(gè)階段完成onRefresh(); // 注冊(cè)監(jiān)聽器// 在所有注冊(cè)的bean 中查找Listener bean , 注冊(cè)到消息廣播報(bào)中registerListeners(); /**第11步對(duì)于非抽象類、非延遲初始化的單例bean,在spring容器啟動(dòng)的時(shí)候調(diào)用getBean方法來實(shí)例化bean, 并進(jìn)行相關(guān)初始化工作,getBean方法最終調(diào)用AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean方法 */// 在創(chuàng)建BeanFactory的過程中,BeanDefinition注冊(cè)到了BeanFactory中的一個(gè)ConCurretHashMap對(duì)象中// 以BeanName為key,BeanDefinition為value ; 實(shí)例化所有剩余的(非延遲初始化)單例。finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // 第12步 最后一步:發(fā)布相應(yīng)的事件。//完成刷新過程, 通知生命周期處現(xiàn)器lifecycleProcessor 刷新過程, 同時(shí)發(fā)出ContextRefreshEvent 通知?jiǎng)e人finishRefresh();} catch (BeansException ex) {if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {logger.warn('Exception encountered during context initialization - ' +'cancelling refresh attempt: ' + ex);} // 第13步 銷毀以創(chuàng)建的BeandestroyBeans(); //取消refresh操作,重置容器的同步標(biāo)識(shí)cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.throw ex;} finally {resetCommonCaches();}}}2.4 AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
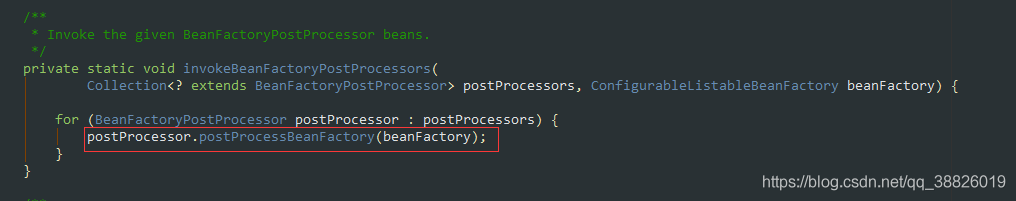
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); // 對(duì)BeanDefinitionRegistry 類型的處理if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();// 用于存放BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessorList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 遍歷所有的beanFactoryPostProcessors,將BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor區(qū)分開for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;/**對(duì)于BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 類型, 在BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的基礎(chǔ)上還有自己定義的方法,需要先調(diào)用 */registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);}else {// 記錄常規(guī)BeanFactoryPostProcessorregularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);}} /**不要在這里初始化FactoryBeans: 我們需要保留所有常規(guī)bean未初始化,讓bean工廠后處理器應(yīng)用到它們!BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors之間的分離實(shí)現(xiàn)排好序,點(diǎn)好,等等。獲取spring配置文件中定義的所有實(shí)現(xiàn)BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean,然后根據(jù)優(yōu)先級(jí)進(jìn)行排序 */List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 首先,調(diào)用實(shí)現(xiàn)優(yōu)先排序的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessorsString[] postProcessorNames =beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {// PriorityOrdered.class 優(yōu)先排序if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));processedBeans.add(ppName);}}sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // 接下來,調(diào)用實(shí)現(xiàn)Ordered的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessorspostProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {// Ordered.classif (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));processedBeans.add(ppName);}}sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.boolean reiterate = true;while (reiterate) {reiterate = false;postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));processedBeans.add(ppName);reiterate = true;}}sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);currentRegistryProcessors.clear();} // Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.// 調(diào)用ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory增強(qiáng)配置類// 通過cglib生成增強(qiáng)類// 設(shè)置beanDefinition的beanClass為增強(qiáng)類,讓@Bean生成的bean是單例invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);} else {// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);} // BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class類型// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!String[] postProcessorNames =beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);// 篩選出bean工程中存在的所有實(shí)現(xiàn)BeanFactoryPostProcessor類的類名稱 // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,// Ordered, and the rest.List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {// skip - already processed in first phase above// 已經(jīng)存在了,不再處理}else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {// 為PriorityOrdered類型priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {// 為Ordered類型orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);}else {// 這個(gè)就是我們當(dāng)前需要關(guān)心的PostProcessors//nonOrderedPostProcessors添加的不是bean實(shí)例,而是BeanDefinitionnonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);}} // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();}2.6 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
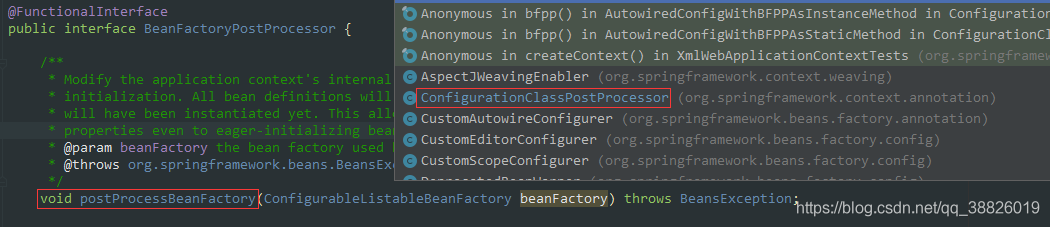
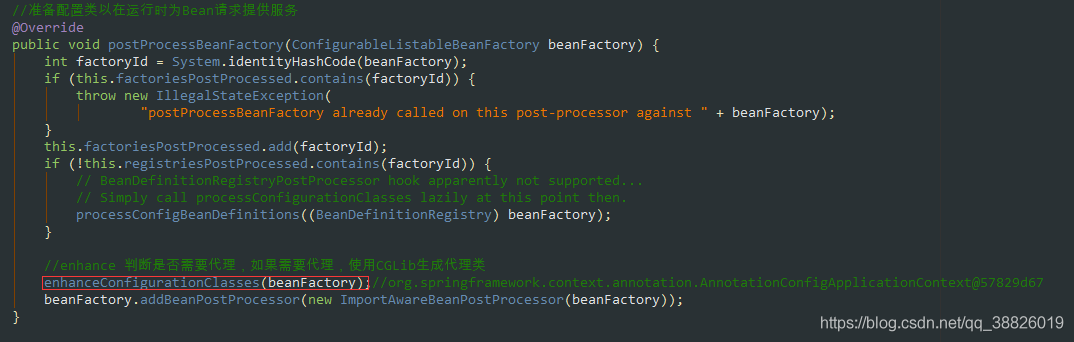
public void enhanceConfigurationClasses(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> configBeanDefs = new LinkedHashMap<>();for (String beanName : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {BeanDefinition beanDef = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);// 判斷是否是一個(gè)全注解類// 掃描是全注解類?full和lite的關(guān)系if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {if (!(beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException('Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition ’' +beanName + '’ since it is not stored in an AbstractBeanDefinition subclass');}else if (logger.isInfoEnabled() && beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) {logger.info('Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition ’' + beanName +'’ since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause ' +'is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor ' +'return type: Consider declaring such methods as ’static’.');}// 是全注解,需要代理,添加到configBeanDefs中configBeanDefs.put(beanName, (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef);}}if (configBeanDefs.isEmpty()) {// nothing to enhance -> return immediatelyreturn;} ConfigurationClassEnhancer enhancer = new ConfigurationClassEnhancer();// 遍歷這個(gè)mapfor (Map.Entry<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> entry : configBeanDefs.entrySet()) {AbstractBeanDefinition beanDef = entry.getValue();// If a @Configuration class gets proxied, always proxy the target classbeanDef.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);try {// Set enhanced subclass of the user-specified bean classClass<?> configClass = beanDef.resolveBeanClass(this.beanClassLoader);if (configClass != null) {// 進(jìn)行cglib代理,為@Configuration注解的類生成增強(qiáng)類Class<?> enhancedClass = enhancer.enhance(configClass, this.beanClassLoader);if (configClass != enhancedClass) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace(String.format('Replacing bean definition ’%s’ existing class ’%s’ with ' +'enhanced class ’%s’', entry.getKey(), configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName()));}// 再通過beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass)修改beanDefinition的BeanClass屬性,// 在bean實(shí)例化階段,會(huì)利用反射技術(shù)將beanClass屬性對(duì)應(yīng)的類實(shí)例化出來// 所以最終實(shí)例化出來的@Configuration bean是一個(gè)代理類的實(shí)例beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass);}}}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new IllegalStateException('Cannot load configuration class: ' + beanDef.getBeanClassName(), ex);}}
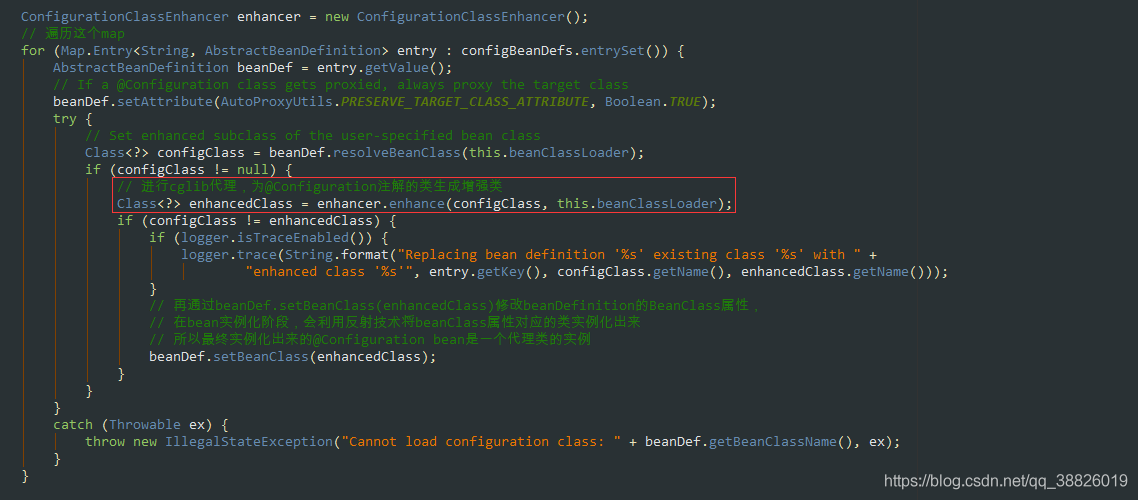
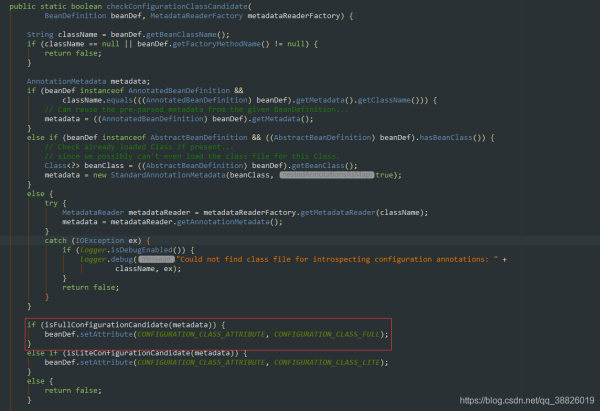

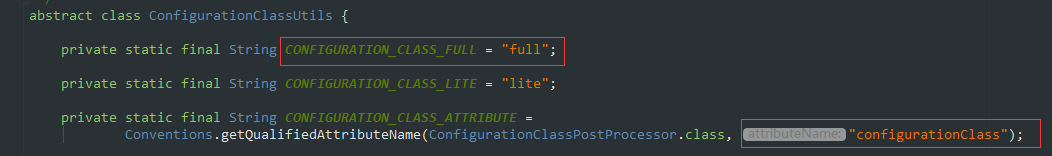
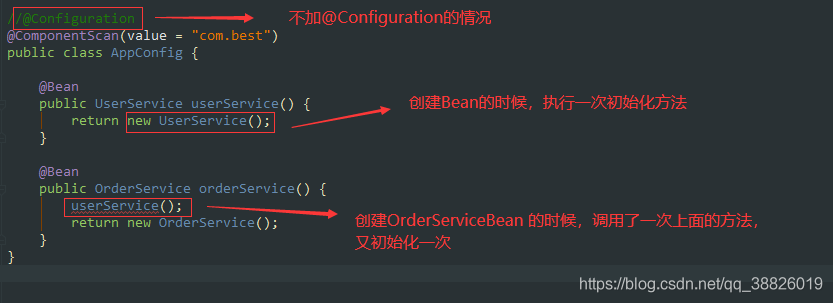
1.在ConfigurationClassUtils類中的checkConfigurationClassCandidate標(biāo)記是Full @Configuration還是lite @Bean mode
2.通過'full'.equals(configClassAttr)判斷是否是全類注解是全注解
3.則將beandefinition放入map中configBeanDefs.put
4.遍歷這個(gè)map
5.使用cglib技術(shù)為配置類生成一個(gè)enhancedClass
6.通過enhancer.enhance進(jìn)行cglib代理,為@Configuration注解的類生成增強(qiáng)類
7.再通過beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass)修改beanDefinition的BeanClass屬性,在bean實(shí)例化階段,會(huì)利用反射技術(shù)將beanClass屬性對(duì)應(yīng)的類實(shí)例化出來,所以最終實(shí)例化出來的@Configuration bean是一個(gè)代理類的實(shí)例
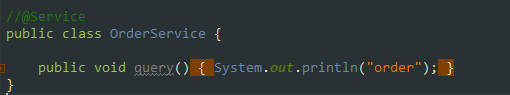
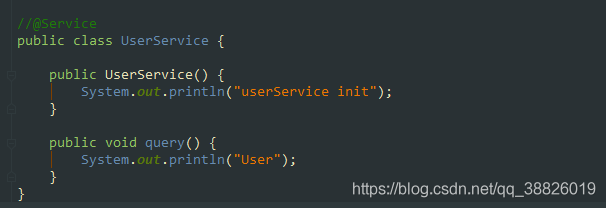
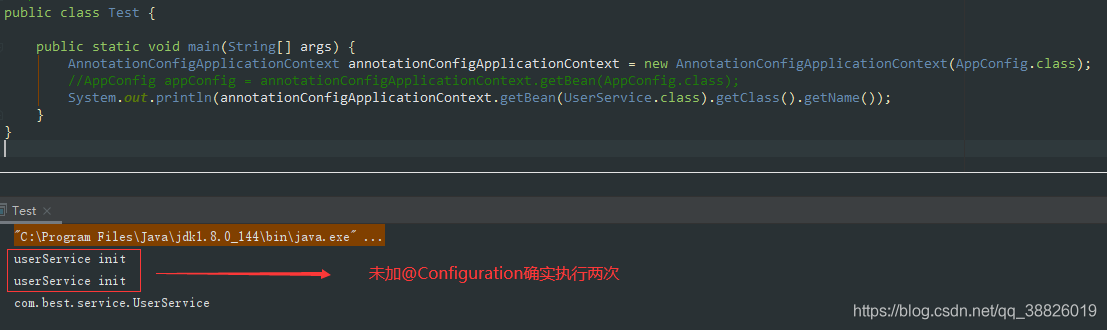
使用了@Configuration注解的類,屬于Full @Configuration。@Configuration類允許通過調(diào)用同一類中的其他@Bean方法來定義bean之間的依賴關(guān)系,保證@Bean的對(duì)象作用域受到控制,避免多例。
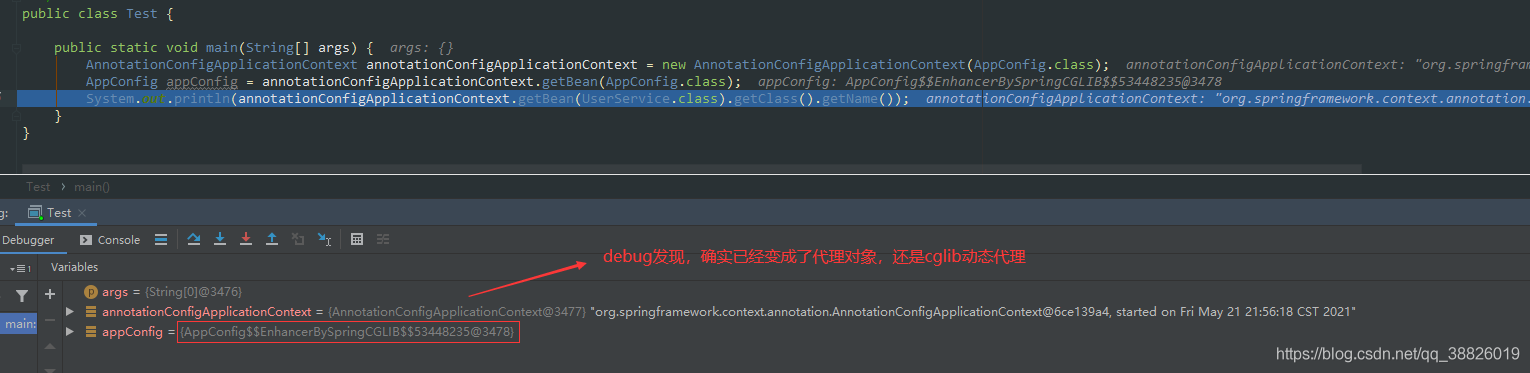
@Configuration類中的@Bean地方會(huì)被CGLIB進(jìn)行代理。Spring會(huì)攔截該方法的執(zhí)行,在默認(rèn)單例情況下,容器中只有一個(gè)Bean,所以我們多次調(diào)用user()方法,獲取的都是同一個(gè)對(duì)象。
對(duì)于@Configuration注解的類中@Bean標(biāo)記的方法,返回的都是一個(gè)bean,在增強(qiáng)的方法中,Spring會(huì)先去容器中查看一下是否有這個(gè)bean的實(shí)例了,如果有了的話,就返回已有對(duì)象,沒有的話就創(chuàng)建一個(gè),然后放到容器中。
2.10 ConfigurationClassEnhancer#enhance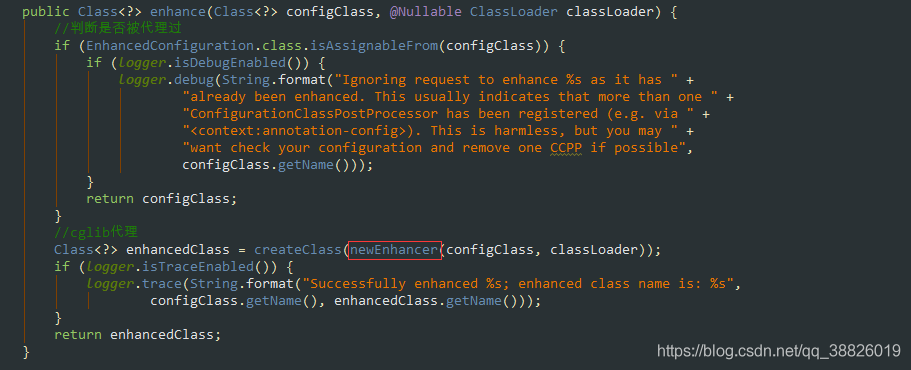
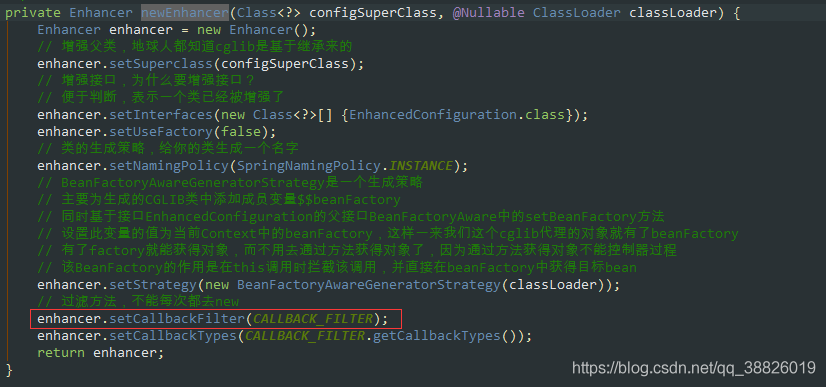
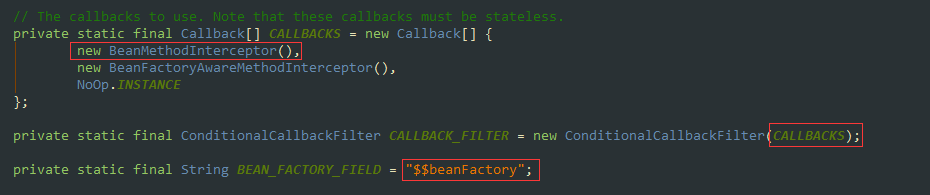
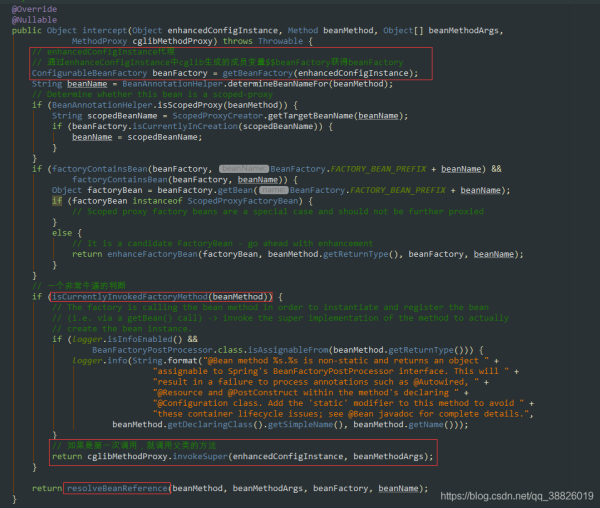
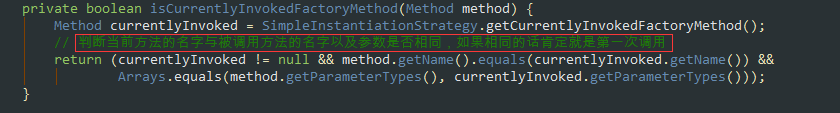
private Object resolveBeanReference(Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs,ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory, String beanName) { // The user (i.e. not the factory) is requesting this bean through a call to// the bean method, direct or indirect. The bean may have already been marked// as ’in creation’ in certain autowiring scenarios; if so, temporarily set// the in-creation status to false in order to avoid an exception.// 判斷他是否正在創(chuàng)建boolean alreadyInCreation = beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(beanName);try {if (alreadyInCreation) {beanFactory.setCurrentlyInCreation(beanName, false);}boolean useArgs = !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(beanMethodArgs);if (useArgs && beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {// Stubbed null arguments just for reference purposes,// expecting them to be autowired for regular singleton references?// A safe assumption since @Bean singleton arguments cannot be optional...for (Object arg : beanMethodArgs) {if (arg == null) {useArgs = false;break;}}}Object beanInstance = (useArgs ? beanFactory.getBean(beanName, beanMethodArgs) :beanFactory.getBean(beanName));if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanInstance)) {// Detect package-protected NullBean instance through equals(null) checkif (beanInstance.equals(null)) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug(String.format('@Bean method %s.%s called as bean reference ' +'for type [%s] returned null bean; resolving to null value.',beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName(),beanMethod.getReturnType().getName()));}beanInstance = null;}else {String msg = String.format('@Bean method %s.%s called as bean reference ' +'for type [%s] but overridden by non-compatible bean instance of type [%s].',beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName(),beanMethod.getReturnType().getName(), beanInstance.getClass().getName());try {BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName);msg += ' Overriding bean of same name declared in: ' + beanDefinition.getResourceDescription();}catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {// Ignore - simply no detailed message then.}throw new IllegalStateException(msg);}}Method currentlyInvoked = SimpleInstantiationStrategy.getCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod();if (currentlyInvoked != null) {String outerBeanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(currentlyInvoked);beanFactory.registerDependentBean(beanName, outerBeanName);}return beanInstance;}finally {if (alreadyInCreation) {beanFactory.setCurrentlyInCreation(beanName, true);}}}三、總結(jié) lite @Bean mode :當(dāng)@Bean方法在沒有使用@Configuration注解的類中聲明時(shí)稱之為lite @Bean mode Full @Configuration:如果@Bean方法在使用@Configuration注解的類中聲明時(shí)稱之為Full @Configuration
Full @Configuration中的@Bean方法會(huì)被CGLIB所代理,而 lite @Bean mode中的@Bean方法不會(huì)被CGLIB代理
@Configuration注解作用
1.告訴spring這是一個(gè)配置類,相當(dāng)于spring的xml配置文件
2.被@Configuration 注解的類,會(huì)被cglib代理進(jìn)行增強(qiáng)
3.@Configuration類允許通過調(diào)用同一類中的其他@Bean方法來定義bean之間的依賴關(guān)系,保證@Bean的對(duì)象作用域受到控制,避免多例
@Configuration注解底層是如何實(shí)現(xiàn)的,通過源碼咱們可以反推并總結(jié)為以下幾點(diǎn):

1.Spring首先會(huì)獲取到所有的beanDefenition
2.ConfigurationClassUtils類中checkConfigurationClassCandidate方法判斷是Full @Configuration還是lite @Bean mode
3.通過ConfigurationClassPostProcessor后置處理器遍歷所有的beanDefenition
4.將標(biāo)記了Full @Configuration模式的beanDefenition,會(huì)對(duì)這個(gè)類進(jìn)行cglib代理,生成一個(gè)代理類,并把這個(gè)類設(shè)置到BeanDefenition的Class屬性中
5.配置類會(huì)被CGLIB增強(qiáng)(生成代理對(duì)象),放進(jìn)IoC容器內(nèi)的是代理
6.對(duì)于內(nèi)部類是沒有限制的:可以是Full模式或者Lite模式
7.配置類內(nèi)部可以通過方法調(diào)用來處理依賴,并且能夠保證是同一個(gè)實(shí)例,都指向IoC內(nèi)的那個(gè)單例
8.需要用這個(gè)Bean實(shí)例的時(shí)候,從這個(gè)Class屬性中拿到的Class對(duì)象進(jìn)行反射,最終反射出來的是代理增強(qiáng)后的類
9.通過@Configuration標(biāo)注類的Bean,Spring會(huì)先去容器中查看是否有這個(gè)Bean實(shí)例,如果有就返回已有的對(duì)象,沒有就創(chuàng)建一個(gè),然后放到容器中
到此這篇關(guān)于Spring源碼解析之Configuration的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Configuration源碼內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. 基于javaweb+jsp實(shí)現(xiàn)學(xué)生宿舍管理系統(tǒng)2. ASP.NET MVC實(shí)現(xiàn)樹形導(dǎo)航菜單3. 多級(jí)聯(lián)動(dòng)下拉選擇框,動(dòng)態(tài)獲取下一級(jí)4. 如何封裝一個(gè)Ajax函數(shù)5. .NET Core中RabbitMQ使用死信隊(duì)列的實(shí)現(xiàn)6. 什么是JWT超詳細(xì)講解7. Python爬蟲基礎(chǔ)之初次使用scrapy爬蟲實(shí)例8. python 在mysql中插入null空值的操作9. Python如何telnet到網(wǎng)絡(luò)設(shè)備10. JavaScript反轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)組常用的4種方法

 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備