Java多線程導致CPU占用100%解決及線程池正確關閉方式
情景:1000萬表數據導入內存數據庫,按分頁大小10000查詢,多線程,15條線程跑。使用了ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(15)本地跑了一段時間后,發現電腦CPU逐漸升高,最后CPU占用100%卡死,內存使用也高達80%。
排查問題Debug 發現雖然創建了定長15的線程池,但是因為數據量大,在For中循環分頁查詢的List會持續加入LinkedBlockingQueue()隊列中每一個等待的任務,又加載了1萬的數據。所以不管是線程數的CPU搶占,還是內存的消耗都是極高。所以是不是能夠控制等待隊列LinkedBlockingQueue的上限就可以了。
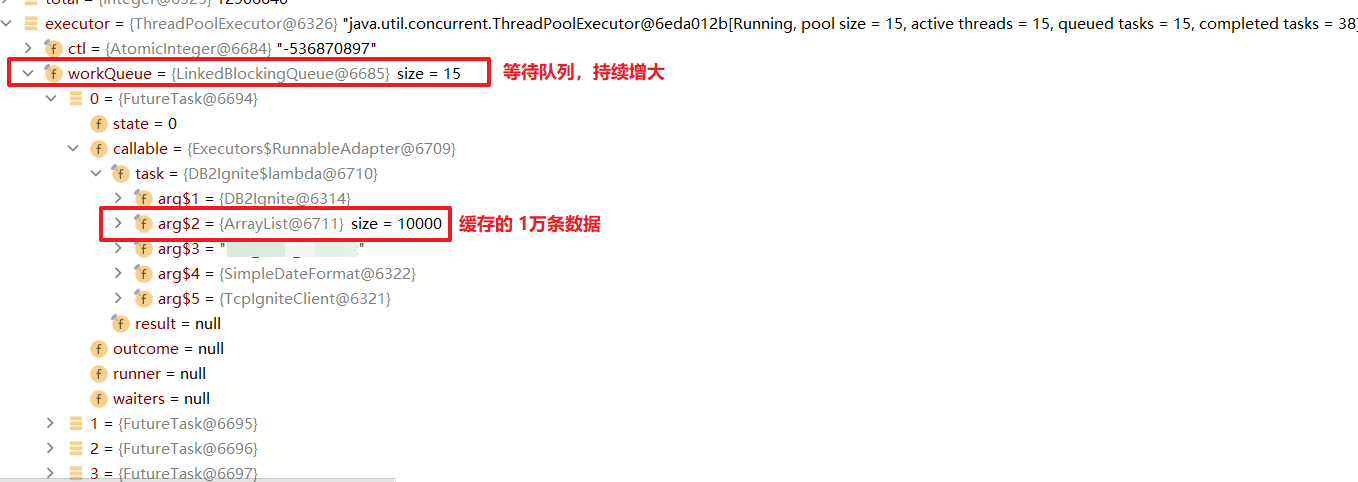
使用AtomicLong 統計線程是否完成,再執行executor.submit()提交新的任務導隊列中。偽代碼如下:
private AtomicLong threadNum = new AtomicLong(0);public void init() throws Exception {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(15);Integer total = accountMapper.selectCount(new QueryWrapper<>());Integer pageSize = 10000; // 頁大小Integer pageCount = (total + pageSize -1) / pageSize; // 總頁數for (Integer start = 1; start <= pageCount; start++) {List<Account> list = accountMapper.selectPage(new Page<>(start, pageSize), query).getRecords();//等待線程任務完成,設置30,可令運行線程數為15,等待隊列線程數為15while (threadNum.get() >= 30){Thread.sleep(5000);}//開啟1個線程+1threadNum.incrementAndGet();executor.submit(() -> {try {// 處理業務dealMessage(list);// 任務完成 -1threadNum.decrementAndGet();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}});}executor.shutdown();executor.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);}
效果就是CPU保持在15~45%之間,內存占用也只有45%。
目前只想到這樣的方式,控制等待隊列LinkedBlockingQueue的上限,還有更好的方式請告知,感謝!
2021-02-03-分割線最近又用到了多線程開發,發現了還是有很多方式控制的。簡單的使用java的Semaphore令牌限流控制也能實現。
多線程: 線程池必須關閉,main主線程才能結束(接口才會返回)finally { executorService.shutdown(); } 主線程等待保證多線程所有子線程任務執行完畢,再結束。 -> executorService.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS); semaphore 令牌限流控制fixedThread線程池,本例子就是最多同時擁有2個線程進行工作 fixedThread.execute() fixedThread.submit() 的差別除了后者可以返回結果外,后者還會catch掉異常信息,無法拋到主線程中。public static void main(String[] args) { final List<String> tableNames = new ArrayList<>(); tableNames.add('a'); tableNames.add('b'); tableNames.add('c'); tableNames.add('d'); tableNames.add('e'); tableNames.add('f'); final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(2); final ExecutorService fixedThread = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for (final String tableName : tableNames) {//阻塞,獲取令牌try { semaphore.acquire();} catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace();}//dofixedThread.execute(() -> { //can throw ex log final ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); try {executorService.submit(() -> { //can’t throw ex log //int i = 1/0; System.out.println('tableName2:' + tableName);});//int i = 1/0;System.out.println('tableName:' + tableName); } catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace(); } finally {executorService.shutdown();try { executorService.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);} catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace();}semaphore.release();System.out.println('semaphore.release'); }}); } // 記得關閉線程池 fixedThread.shutdown(); try {fixedThread.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS); } catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println('主線程...');}
打印結果
tableName:btableName2:btableName:atableName2:asemaphore.releasesemaphore.releasetableName:dtableName2:dtableName:csemaphore.releasetableName:etableName2:csemaphore.releasetableName:ftableName2:esemaphore.releasetableName2:fsemaphore.release主線程...
到此這篇關于Java多線程導致CPU占用100%解決及線程池正確關閉方式的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Java多線程CPU占用100%內容請搜索好吧啦網以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網!
相關文章:
1. 基于javaweb+jsp實現企業車輛管理系統2. 怎樣才能用js生成xmldom對象,并且在firefox中也實現xml數據島?3. 利用ajax+php實現商品價格計算4. ASP.Net MVC利用NPOI導入導出Excel的示例代碼5. jstl 字符串處理函數6. JSP動態網頁開發原理詳解7. PHP中為什么使用file_get_contents("php://input")接收微信通知8. .Net core Blazor+自定義日志提供器實現實時日志查看器的原理解析9. IOS蘋果AppStore內購付款的服務器端php驗證方法(使用thinkphp)10. XML CDATA是什么?
 網公網安備
網公網安備