python使用多線程查詢數(shù)據(jù)庫的實(shí)現(xiàn)示例
一.背景:
當(dāng)數(shù)據(jù)量過大時,一個程序的執(zhí)行時間就會主要花費(fèi)在等待單次查詢返回結(jié)果,在這個過程中cpu無疑是處于等待io的空閑狀態(tài)的,這樣既浪費(fèi)了cpu資源,又花費(fèi)了大量時間(當(dāng)然這里主要說多線程,批量查詢不在考慮范圍,總會存在不能批量查詢的情況),在這種非密集型運(yùn)算(及大量占用cpu資源)的情況下在python中無疑運(yùn)用多線程是一個非常棒的選擇。
二.知識點(diǎn):
數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池的運(yùn)用及優(yōu)勢,python中多線程的運(yùn)用,隊(duì)列的運(yùn)用
數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池:限制了數(shù)據(jù)庫的連接最大個數(shù),每次連接都是可以重復(fù)使用的,當(dāng)然也可以限制每個連接的重復(fù)使用次數(shù)(這個在這里是沒必要的),需要注意的是設(shè)置的數(shù)據(jù)庫的最大連接個數(shù)最好要大于我們自己開的最大線程個數(shù),一般邏輯是每個線程占用一個數(shù)據(jù)庫連接可以使程序達(dá)到最大速度,如果小于則可能存在同時連接個數(shù)大于數(shù)據(jù)庫允許的最大連接個數(shù)的風(fēng)險。使用數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池的優(yōu)勢在于,python多線程并發(fā)操作數(shù)據(jù)庫,會存在鏈接數(shù)據(jù)庫超時、數(shù)據(jù)庫連接丟失、數(shù)據(jù)庫操作超時等問題,而數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池提供線程間可共享的數(shù)據(jù)庫連接,并自動管理連接。
python多線程:在程序等待io的時間里調(diào)用多線程去數(shù)據(jù)庫執(zhí)行查詢操作。
隊(duì)列:這個就是數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)里面的知識了,一般隊(duì)列的常用模式先進(jìn)先出隊(duì)列。(這里主要用的是隊(duì)列取一個數(shù)就少一個數(shù)的原理,其實(shí)用列表也可以實(shí)現(xiàn),他的先進(jìn)先出主要強(qiáng)調(diào)的是一個順序關(guān)系,這一點(diǎn)到?jīng)]用上,就當(dāng)是練練手了)
三.兩段代碼作比較:
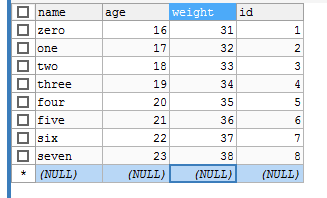
數(shù)據(jù)庫的截圖:
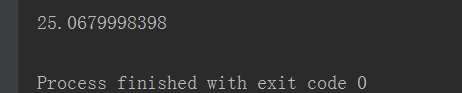
第一段代碼:正常循環(huán)查詢并打印出執(zhí)行時間
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-import timeimport threadingimport MySQLdbimport Queuefrom MySQLdb.cursors import DictCursorfrom DBUtils.PooledDB import PooledDBdef mysql_connection(): host = ’localhost’ user = ’root’ port = 3306 password = ’123456’ db = ’test’ charset = ’utf8’ limit_count = 3 # 最低預(yù)啟動數(shù)據(jù)庫連接數(shù)量 pool = PooledDB(MySQLdb, limit_count, maxconnections=15, host=host, user=user, port=port, passwd=password, db=db, charset=charset, use_unicode=True, cursorclass=DictCursor) return poolstart = time.time()pool = mysql_connection()for id in range(50): con = pool.connection() cur = con.cursor() sql = ’’’select id,name,age,weight from test where id = %s ’’’%id cur.execute(sql) time.sleep(0.5) result = cur.fetchall() if result: print(’this is tread %s (%s,%s,%s,%s)’%(id,result[0][’id’],result[0][’name’],result[0][’age’],result[0][’weight’])) else: print(’this tread %s result is none’%id)end = time.time() - startprint(end)
執(zhí)行結(jié)果:
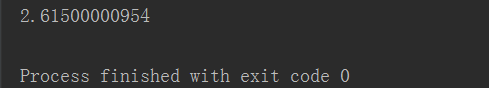
第二段代碼:限制數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池最大15個連接,用隊(duì)列限制最大線程個數(shù)為10個
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-import timeimport threadingimport MySQLdbimport Queuefrom MySQLdb.cursors import DictCursorfrom DBUtils.PooledDB import PooledDBdef mysql_connection(): host = ’localhost’ user = ’root’ port = 3306 password = ’123456’ db = ’test’ charset = ’utf8’ limit_count = 3 # 最低預(yù)啟動數(shù)據(jù)庫連接數(shù)量 pool = PooledDB(MySQLdb, limit_count, maxconnections=15, host=host, user=user, port=port, passwd=password, db=db, charset=charset, use_unicode=True, cursorclass=DictCursor) return pooldef tread_connection_db(id): con = pool.connection() cur = con.cursor() sql = ’’’select id,name,age,weight from test where id = %s ’’’%id cur.execute(sql) time.sleep(0.5) result = cur.fetchall() if result: print(’this is tread %s (%s,%s,%s,%s)’%(id,result[0][’id’],result[0][’name’],result[0][’age’],result[0][’weight’])) else: print(’this tread %s result is none’%id) con.close()if __name__==’__main__’: start = time.time() #創(chuàng)建線程連接池,最大限制15個連接 pool = mysql_connection() #創(chuàng)建隊(duì)列,隊(duì)列的最大個數(shù)及限制線程個數(shù) q=Queue.Queue(maxsize=10) #測試數(shù)據(jù),多線程查詢數(shù)據(jù)庫 for id in range(50): #創(chuàng)建線程并放入隊(duì)列中 t = threading.Thread(target=tread_connection_db, args=(id,)) q.put(t) #隊(duì)列隊(duì)滿 if q.qsize()==10: #用于記錄線程,便于終止線程 join_thread = [] #從對列取出線程并開始線程,直到隊(duì)列為空 while q.empty()!=True:t = q.get()join_thread.append(t)t.start() #終止上一次隊(duì)滿時里面的所有線程 for t in join_thread:t.join() end = time.time() - start print(end)
程序備注應(yīng)該還算比較清晰的哈,程序執(zhí)行結(jié)果:
四.結(jié)論:
看結(jié)果說話
到此這篇關(guān)于python使用多線程查詢數(shù)據(jù)庫的實(shí)現(xiàn)示例的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)python 多線程查詢數(shù)據(jù)庫內(nèi)容請搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. jstl 字符串處理函數(shù)2. JSP動態(tài)網(wǎng)頁開發(fā)原理詳解3. XHTML 1.0:標(biāo)記新的開端4. Vue中使用Echarts儀表盤展示實(shí)時數(shù)據(jù)的實(shí)現(xiàn)5. 深入理解JavaScript中的Base64編碼字符串6. java 字符串轉(zhuǎn)化為字符數(shù)組的3種實(shí)現(xiàn)案例7. JSP頁面的靜態(tài)包含和動態(tài)包含使用方法8. WAP建站W(wǎng)ML語言語法基礎(chǔ)教程第1/6頁9. 基于python實(shí)現(xiàn)判斷字符串是否數(shù)字算法10. PHP擴(kuò)展之URL編碼、解碼及解析——URLs

 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備