python matplotlib工具欄源碼探析二之添加、刪除內置工具項的案例
從matplotlib工具欄源碼探析一(禁用工具欄、默認工具欄和工具欄管理器三種模式的差異)一文可知matplotlib內置實現了多個工具項的實現,而默認工具欄中的工具項只是其中的一部分,有沒有方法直接管理工具欄,添加、刪除內置工具項?
matplotlib內置的工具項由源碼可知,matplotlib.backend_tools.default_tools變量為字典類型,實例化了基于matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolBase類定義的內置工具項。
源碼
default_tools = {’home’: ToolHome, ’back’: ToolBack, ’forward’: ToolForward, ’zoom’: ToolZoom, ’pan’: ToolPan, ’subplots’: ’ToolConfigureSubplots’, ’save’: ’ToolSaveFigure’, ’grid’: ToolGrid, ’grid_minor’: ToolMinorGrid, ’fullscreen’: ToolFullScreen, ’quit’: ToolQuit, ’quit_all’: ToolQuitAll, ’allnav’: _ToolEnableAllNavigation, ’nav’: _ToolEnableNavigation, ’xscale’: ToolXScale, ’yscale’: ToolYScale, ’position’: ToolCursorPosition, _views_positions: ToolViewsPositions, ’cursor’: ’ToolSetCursor’, ’rubberband’: ’ToolRubberband’, ’help’: ’ToolHelp’, ’copy’: ’ToolCopyToClipboard’, }
驗證
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib as mplfrom pprint import pprintplt.rcParams[’toolbar’] = ’toolmanager’fig = plt.gcf()pprint(mpl.backend_tools.default_tools)
輸出
{’allnav’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools._ToolEnableAllNavigation’>, ’back’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolBack’>, ’copy’: ’ToolCopyToClipboard’, ’cursor’: ’ToolSetCursor’, ’forward’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolForward’>, ’fullscreen’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolFullScreen’>, ’grid’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolGrid’>, ’grid_minor’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolMinorGrid’>, ’help’: ’ToolHelp’, ’home’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolHome’>, ’nav’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools._ToolEnableNavigation’>, ’pan’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolPan’>, ’position’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolCursorPosition’>, ’quit’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolQuit’>, ’quit_all’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolQuitAll’>, ’rubberband’: ’ToolRubberband’, ’save’: ’ToolSaveFigure’, ’subplots’: ’ToolConfigureSubplots’, ’viewpos’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolViewsPositions’>, ’xscale’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolXScale’>, ’yscale’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolYScale’>, ’zoom’: <class ’matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolZoom’>}
使用工具欄管理器管理內置工具項
由源碼可知默認工具欄模式toolbar2模式沒有提供添加、刪除工具項的接口。因此,管理工具欄需要使用工具欄管理器模式toolmanager,與該模式相關的重要定義有:
matplotlib.backend_bases.ToolContainerBase(toolmanager)類:工具欄容器的基類,定義了工具欄編輯的方法。構造函數參數為toolmanager,表示工具欄容器容納的工具欄。 matplotlib.backend_managers.ToolManager(figure=None)類:管理用戶觸發工具欄工具項按鈕而產生的動作。matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolBase類:所有工具欄工具項的基類,所有工具項均由matplotlib.backend_managers.ToolManager實例化。 matplotlib.backend_tools.default_tools變量:字典類型,實例化基于matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolBase類定義的內置工具項。 matplotlib.backend_tools.default_toolbar_tools變量:嵌套列表,以類似格式[[分組1, [工具1, 工具2 ...]], [分組2, [...]]]定義工具欄布局。 matplotlib.backend_tools.add_tools_to_container函數:設置toolbarmanager模式默認工具欄。使用系統函數實現添加工具項根據源碼可知,matplotlib.backend_tools.add_tools_to_container函數可以設置toolbarmanager模式默認工具欄。
案例
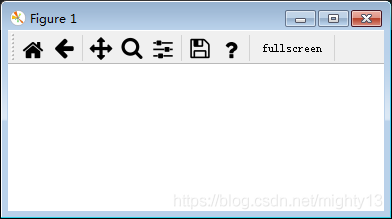
案例說明:為工具欄添加全屏切換工具項。
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib as mplplt.rcParams[’toolbar’] = ’toolmanager’fig = plt.gcf()# 通過mpl.backend_tools.add_tools_to_container函數添加工具項mpl.backend_tools.add_tools_to_container(fig.canvas.manager.toolbar, tools=[[’foo’, [ ’fullscreen’]]])plt.show()
案例解析:add_tools_to_container函數有兩個參數container和tools,由源碼可知container參數的值應為fig.canvas.manager.toolbar,tools參數按照[[分組1, [工具1, 工具2 ...]], [分組2, [...]]]格式取值。
根據源碼可知:
添加內置工具項有兩種方法
toolbar對象可以通過add_tool方法添加內置工具項,參數為name和tool,name為工具項的名稱,tool為添加的工具項對應的類或者字符串。 toolbar對象可以通過add_toolitem方法添加內置工具項,參數為name、group、 position、 image_file、 description和 toggle,name為工具項的名稱,group為工具項所在組,position為工具項在組中的位置,取值為列表索引,一般取-1即在所在組末尾追加,設置為0即在所在組的首位,image_file為工具項圖像,值為字符串,description為工具項描述, toggle為是否為切換式工具項,布爾值。 刪除內置工具項有兩種方法 toolbar對象可以通過remove_toolitem方法刪除內置工具項,參數為name,即工具項的名稱。 toolmanager對象可以通過remove_tool方法刪除內置工具項,參數為name,即工具項的名稱。案例案例說明:刪除向前工具項,添加全屏切換工具項。
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib as mplplt.rcParams[’toolbar’] = ’toolmanager’fig = plt.gcf()fig.canvas.manager.toolmanager.remove_tool(’forward’)fig.canvas.manager.toolbar.remove_toolitem(’back’)fig.canvas.manager.toolbar.add_tool(’quit’, ’foo’)fig.canvas.manager.toolbar.add_toolitem(’fullscreen’, ’foo’, -1,’fullscreen’,’fullscreen’,False) plt.show()
通過工具欄管理器添加、刪除內置工具項的方法很多種,需要注意調用對象、方法、參數,閱讀下面的matplotlib源碼可能會有所啟發。
相關源碼matplotlib.backends.backend_qt5模塊
class FigureManagerQT(FigureManagerBase): self.toolbar = self._get_toolbar(self.canvas, self.window) if self.toolmanager: backend_tools.add_tools_to_manager(self.toolmanager) if self.toolbar: backend_tools.add_tools_to_container(self.toolbar) if self.toolbar: self.window.addToolBar(self.toolbar) tbs_height = self.toolbar.sizeHint().height() else: tbs_height = 0
def _get_toolbar(self, canvas, parent): # must be inited after the window, drawingArea and figure # attrs are set if matplotlib.rcParams[’toolbar’] == ’toolbar2’: toolbar = NavigationToolbar2QT(canvas, parent, True) elif matplotlib.rcParams[’toolbar’] == ’toolmanager’: toolbar = ToolbarQt(self.toolmanager, self.window) else: toolbar = None return toolbar
class ToolbarQt(ToolContainerBase, QtWidgets.QToolBar): def __init__(self, toolmanager, parent): ToolContainerBase.__init__(self, toolmanager) QtWidgets.QToolBar.__init__(self, parent) self.setAllowedAreas( QtCore.Qt.TopToolBarArea | QtCore.Qt.BottomToolBarArea) message_label = QtWidgets.QLabel('') message_label.setAlignment( QtCore.Qt.AlignRight | QtCore.Qt.AlignVCenter) message_label.setSizePolicy( QtWidgets.QSizePolicy(QtWidgets.QSizePolicy.Expanding, QtWidgets.QSizePolicy.Ignored)) self._message_action = self.addWidget(message_label) self._toolitems = {} self._groups = {} def add_toolitem( self, name, group, position, image_file, description, toggle): button = QtWidgets.QToolButton(self) if image_file: button.setIcon(NavigationToolbar2QT._icon(self, image_file)) button.setText(name) if description: button.setToolTip(description) def handler(): self.trigger_tool(name) if toggle: button.setCheckable(True) button.toggled.connect(handler) else: button.clicked.connect(handler) self._toolitems.setdefault(name, []) self._add_to_group(group, name, button, position) self._toolitems[name].append((button, handler)) def _add_to_group(self, group, name, button, position): gr = self._groups.get(group, []) if not gr: sep = self.insertSeparator(self._message_action) gr.append(sep) before = gr[position] widget = self.insertWidget(before, button) gr.insert(position, widget) self._groups[group] = gr def toggle_toolitem(self, name, toggled): if name not in self._toolitems: return for button, handler in self._toolitems[name]: button.toggled.disconnect(handler) button.setChecked(toggled) button.toggled.connect(handler) def remove_toolitem(self, name): for button, handler in self._toolitems[name]: button.setParent(None) del self._toolitems[name] def set_message(self, s): self.widgetForAction(self._message_action).setText(s
matplotlib.backend_tools模塊
def add_tools_to_container(container, tools=default_toolbar_tools): ''' Add multiple tools to the container. Parameters ---------- container : Container `backend_bases.ToolContainerBase` object that will get the tools added. tools : list, optional List in the form ``[[group1, [tool1, tool2 ...]], [group2, [...]]]`` where the tools ``[tool1, tool2, ...]`` will display in group1. See `add_tool` for details. ''' for group, grouptools in tools: for position, tool in enumerate(grouptools): container.add_tool(tool, group, position)
def add_tools_to_manager(toolmanager, tools=default_tools): ''' Add multiple tools to a `.ToolManager`. Parameters ---------- toolmanager : `.backend_managers.ToolManager` Manager to which the tools are added. tools : {str: class_like}, optional The tools to add in a {name: tool} dict, see `add_tool` for more info. ''' for name, tool in tools.items(): toolmanager.add_tool(name, tool)
到此這篇關于python matplotlib工具欄源碼探析二之添加、刪除內置工具項的案例的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關python matplotlib內置工具項內容請搜索好吧啦網以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網!
相關文章:

 網公網安備
網公網安備