Python 使用 consul 做服務發現示例詳解
前面一章講了微服務的一些優點和缺點,那如何做到
一、目標二、使用步驟1. 安裝 consul我們可以直接使用官方提供的二進制文件來進行安裝部署,其官網地址為 https://www.consul.io/downloads
下載后為可執行文件,在我們開發試驗過程中,可以直接使用 consul agent -dev 命令來啟動一個單節點的 consul
在啟動的打印日志中可以看到 agent: Started HTTP server on 127.0.0.1:8500 (tcp), 我們可以在瀏覽器直接訪問 127.0.0.1:8500 即可看到如下
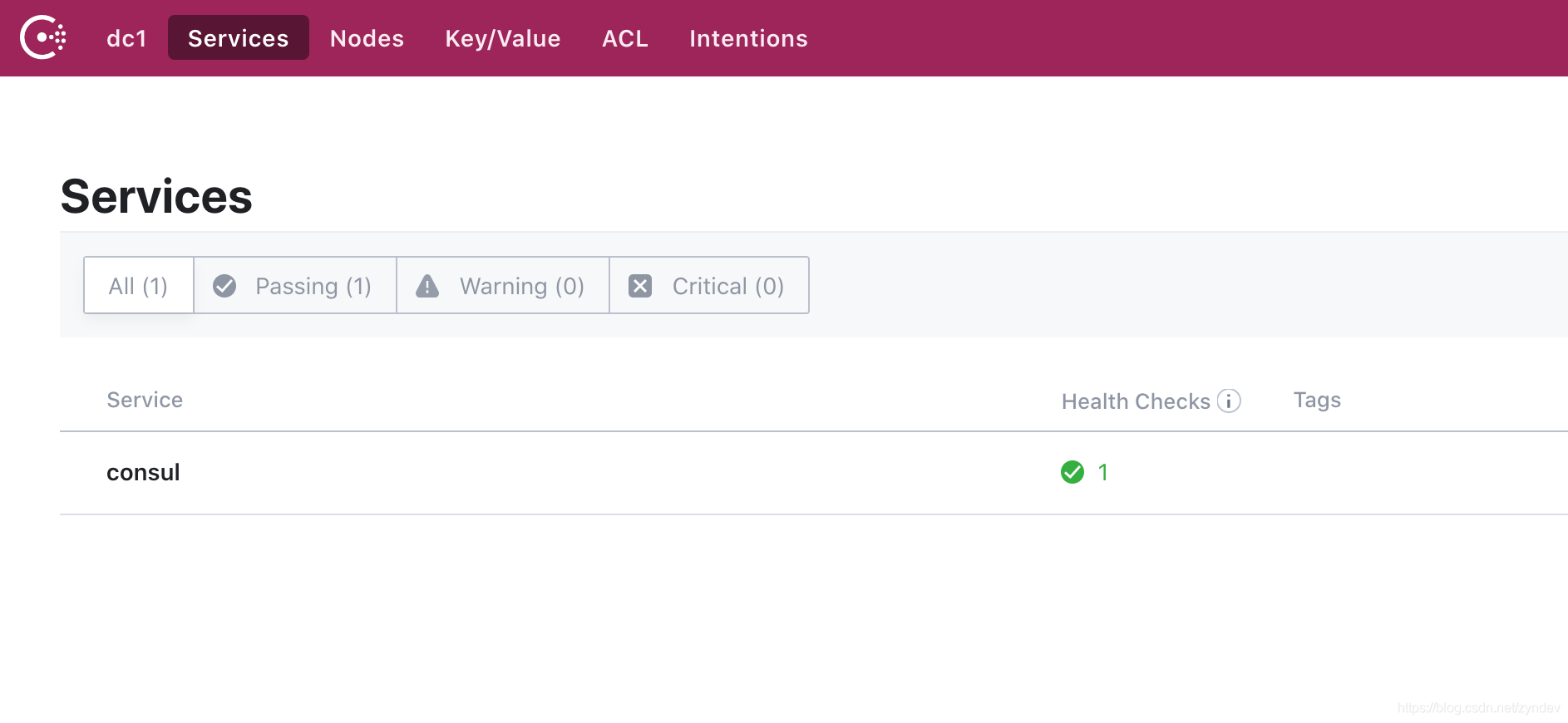
這里我們的 consul 就啟動成功了
2. 服務注冊在網絡編程中,一般會提供項目的 IP、PORT、PROTOCOL,在服務治理中,我們還需要知道對應的服務名、實例名以及一些自定義的擴展信息
在這里使用 ServiceInstance 接口來規定注冊服務時必須的一些信息
class ServiceInstance: def __init__(self, service_id: str, host: str, port: int, secure: bool = False, metadata: dict = None, instance_id: str = None): self.service_id = service_id self.host = host self.port = port self.secure = secure self.metadata = metadata self.instance_id = instance_id def get_instance_id(self): return
定義基類
在上面規定了需要注冊的服務的必要信息,下面定義下服務注冊和剔除的方法,方便以后實現 Eureka 和 Redis 的方式
import abcclass ServiceRegistry(abc.ABC): @abc.abstractmethod def register(self, service_instance: ServiceInstance): pass @abc.abstractmethod def deregister(self): pass
具體實現
因為 consul 提供了 http 接口來對consul 進行操作,我們也可以使用 http 請求方式進行注冊和剔除操作,具體 http 接口文檔見 https://www.consul.io/api-docs, consul 并沒有提供 Python 語言的實現,這里使用 python-consul 來訪問 consul
import consulclass ConsulServiceRegistry(ServiceRegistry): _consul = None _instance_id = None def __init__(self, host: str, port: int, token: str = None): self.host = host self.port = port self.token = token self._consul = consul.Consul(host, port, token=token) def register(self, service_instance: ServiceInstance): schema = 'http' if service_instance.secure: schema = 'https' check = consul.Check.http(f’{schema}:{service_instance.host}:{service_instance.port}/actuator/health’, '1s', '3s', '10s') self._consul.agent.service.register(service_instance.service_id, service_id=service_instance.instance_id, address=service_instance.host, port=service_instance.port, check=check) self._instance_id = service_instance.instance_id def deregister(self): if self._instance_id: self._consul.agent.service.deregister(service_id=self._instance_id) self._instance_id = None3. 服務發現
在服務發現中,一般會需要兩個方法
獲取所有的服務列表 獲取指定的服務的所有實例信息基類定義
import abcclass DiscoveryClient(abc.ABC): @abc.abstractmethod def get_services(self) -> list: pass @abc.abstractmethod def get_instances(self, service_id: str) -> list: pass
具體實現
來實現一下
這里是簡化版,所以一些參數直接寫死了,如果需要可以適當修改
import consulclass ConsulServiceDiscovery(DiscoveryClient): _consul = None def __init__(self, host: str, port: int, token: str = None): self.host = host self.port = port self.token = token self._consul = consul.Consul(host, port, token=token) def get_services(self) -> list: return self._consul.catalog.services()[1].keys() def get_instances(self, service_id: str) -> list: origin_instances = self._consul.catalog.service(service_id)[1] result = [] for oi in origin_instances: result.append(ServiceInstance( oi.get(’ServiceName’), oi.get(’ServiceAddress’), oi.get(’ServicePort’), oi.get(’ServiceTags’), oi.get(’ServiceMeta’), oi.get(’ServiceID’), )) return result4. 測試用例
import unittestfrom random import randomclass MyTestCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_consul_register(self): instance = ServiceInstance('abc', '127.0.0.1', 8000, instance_id=f’abc_{random()}’) registry = ConsulServiceRegistry('127.0.0.1', 8500) discovery = ConsulServiceDiscovery('127.0.0.1', 8500) registry.register(instance) print(discovery.get_services()) print(discovery.get_instances('abc')) self.assertEqual(True, True)if __name__ == ’__main__’: unittest.main()總結
通過使用 consul api 我們可以簡單的實現基于 consul 的服務發現,在通過結合 http rpc 就可簡單的實現服務的調用,下面一章來簡單講下 go 如何發起 http 請求,為我們做 rpc 做個鋪墊
具體代碼見 https://github.com/zhangyunan1994/gimini
參考
https://www.consul.io/api-docs
https://github.com/hashicorp/consul/tree/master/api
到此這篇關于Python 使用 consul 做服務發現的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Python 使用 consul 服務內容請搜索好吧啦網以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網!
相關文章:
 網公網安備
網公網安備